NVIDIA Rubin Platform, Open Models, Autonomous Driving: NVIDIA Presents Blueprint for the Future at CES

NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang took the stage at Fontainebleau Las Vegas today to open CES 2026, announcing that AI is reaching all domains and all devices.
“Computing has been fundamentally changed because of fast computing, because of artificial intelligence,” Huang said. “That means that about ten billion dollars or more of the last decade of computing is now being modernized with this new way of computing.”
Huang unveiled Rubin, NVIDIA's first highly coded, six-chip AI platform now in full production, and introduced Alpamayo, an open-concept family model for autonomous vehicle development — part of a larger push to bring AI to all domains.
Noting that 80% of startups build on open models, Huang reiterated the role of NVIDIA's open models in all domains, trained on NVIDIA supercomputers, creating a global intelligence ecosystem that developers and businesses can build on.
“Every six months, a new model comes out, and these models are getting smarter and smarter,” Huang said. “As a result, you can see the number of downloads explode.”
Get all the NVIDIA news from CES here online press kit.
A New Intelligence Engine: The Rubin Platform
Introducing the audience to the pioneering American astronomer Vera Rubin, after whom NVIDIA named its next-generation computing platform, Huang announced that the NVIDIA Rubin platform, which followed NVIDIA Blackwell's record-breaking design and the company's first ultra-signature, six-chip AI platform, is now in full production.
Built from the data center out, the Rubin platform spans:
- Ruby GPUs with 50 petaflops of NVFP4 inference
- Multiple CPUs designed to move data and process the agent
- NVLink 6 expand the network
- Spectrum‑X Ethernet Photonics free the network
- ConnectX‑9 SuperNICs
- BlueField-4 DPUs
Extreme codesign – designing all these components together – is important because scaling AI at gigascale requires tightly integrated innovation across chips, trays, racks, network, storage and software to eliminate bottlenecks and significantly reduce training and reference costs, Huang explained.
He also introduced AI-native storage with the NVIDIA Inference Context Memory Storage Platform — AI-native KV‑tier storage that improves long content inference with 5x higher tokens per second, 5x better performance per TCO dollar and 5x better energy efficiency.
Put it all together and the Rubin platform promises to significantly accelerate AI innovation, delivering AI tokens at one-tenth the price. “The sooner you train AI models, the sooner you can find the next frontier in the world,” Huang said. “This is your marketing moment. This is technology leadership.”
Open Models For All
NVIDIA's open models – trained on NVIDIA supercomputers – are enabling breakthroughs across healthcare, climate science, robotics, artificial intelligence and automated driving.
“Now on top of this platform, NVIDIA is a frontier AI builder, and we're building in a very special way. We're building completely in an open environment so that we can make all companies, all industries, all countries, be part of this AI revolution.”
The portfolio includes six domains – Clara for healthcare, Earth-2 for climate science, Nemotron for thinking and multimodal AI, Cosmos for robotics and simulation, GR00T for integrated intelligence and Alpamayo for autonomous driving – creating a foundation for innovation in all industries.
“These models are open to the whole world,” Huang said, emphasizing NVIDIA's role as a frontier AI developer with state-of-the-art leaderboards. “You can build a model, test it, monitor it and use it.”
AI Across the Desk: RTX, DGX Spark and Personal Agents
Huang emphasized that the future of AI is not just about supercomputers – it is personal.
Huang showed a demo with a personal AI agent running locally on the NVIDIA DGX Spark desktop supercomputer and integrated with a Reachy Mini robot using Hugging Face models – showing how open models, model routing and local execution turn agents into responsive, portable participants.
“The amazing thing is that it's a small thing now, and yet, a few years ago, that would have been unthinkable, unthinkable,” Huang said.
The world's leading enterprises are integrating NVIDIA AI to power their products, Huang said, citing companies including Palantir, ServiceNow, Snowflake, CodeRabbit, CrowdStrike, NetApp and Semantec.
“Whether it's Palantir or Snowflake or Snowflake – and many other companies we work with – the agent system is the interface.”
At CES, NVIDIA also announced that DGX Spark delivers up to 2.6x performance on larger models, with new support for Lightricks LTX‑2 and FLUX graphics models, and the upcoming availability of NVIDIA AI Enterprise.
Physical AI
AI is now rooted in the physical world, with NVIDIA's training, prediction and computing technology.
These systems can be trained on artificial data in the virtual world long before interacting with the real world.
Huang demonstrated NVIDIA Cosmos open-source world models trained with videos, robotics data and simulations. Cosmos:
- Produces realistic videos with a single image
- Includes driving conditions for multiple cameras
- The models are limited to the location of the location from the information of the location
- Performs physical reasoning and trajectory prediction
- It drives an interactive, closed-loop simulation
Taking this story further, Huang announced Alpamayo, an open portfolio of conceptual language action models, simulation plans and datasets that enable level 4 skill autonomy. This includes:
- Alpamayo R1 – the first open, conceptual model of VLA for automatic driving
- AlpaSim — a fully open simulation platform for high-fidelity AV testing
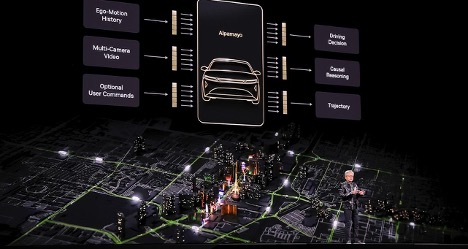
“It's not just taking sensor input and turning on the steering, brakes and speed, and it's defining what action to take,” Huang said, including a video showing the car moving smoothly through San Francisco traffic.
Huang announced that the first passenger car equipped with Alpamayo built on NVIDIA DRIVE full stack of autonomous vehicles will be on the road soon in the new Mercedes-Benz CLA – with AI-defined driving coming to the US this year, and following the latest EuroNCAP rating of five stars.
Huang also highlighted the growing momentum behind DRIVE Hyperion, an open, modular, level-4 platform that has been adopted by leading automotive manufacturers, suppliers and robotics providers around the world.
“Our vision is, one day, every car, every truck will be autonomous, and we're working towards that future,” Huang said.
Huang was then joined on stage by tiny, hopping, hopping robots as he explained how NVIDIA's full-stack approach is fueling the world's AI ecosystem.
Huang wrapped up a video showing how robots are trained in NVIDIA Isaac Sim and Isaac Lab in photorealistic, simulated worlds — before highlighting the work of partners in virtual AI across the industry, including Synopsis and Cadence, Boston Dynamics and Franka, and more.
He also announced an expanded partnership with Siemens, supported by a montage showing how NVIDIA's full stack integrates with Siemens' industrial software, enabling physical AI in design and manufacturing simulation.
“These manufacturing plants will be giant robots,” Huang said.
Building the Future, Together
Huang explained that NVIDIA builds all systems now because it takes a full stack, optimized to deliver AI success.
“Our job is to make the whole stack so that you all can make amazing requests around the world,” he said.
Watch a replay of the key note:



